buy diflucan online buy diflucan online no prescription
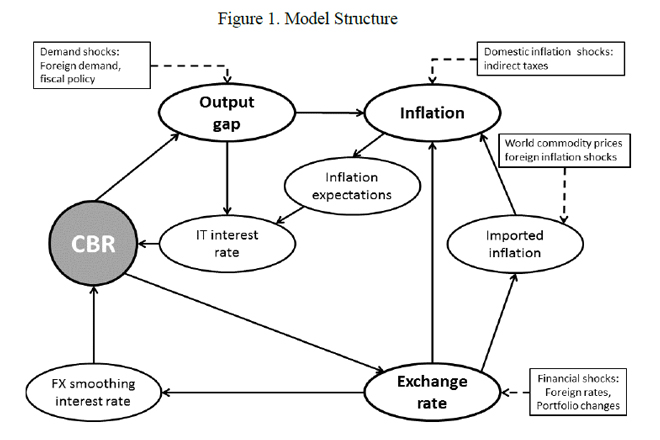
“However, in the move towards the adoption of a Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) regime, it is essential that a more structured approach is employed in analyzing policy trade-offs and macroeconomic dynamics for monetary policy decision purposes.” IMF working paper said a clear logical and a practical policy framework should be in place to support the communication of policy to the public at large. The working paper describes a basic version of a new core forecasting model to be used at the Central Bank for forecasting and monetary policy analysis. The work on this new core model has been part of a broader joint project of the Central Bank and the IMF on developing a modern Forecasting and Policy Analysis System (FPAS). “The development of a (semi-)structural core forecasting model for the FPAS is an essential ingredient to Sri Lanka’s successful transition to FIT,” the working paper said. “This new model will enable holistic analysis in the form of a baseline assessment, balance of risks to the baseline projections while allowing analysis of the nature of policy response to various kinds of shocks.” The model includes a forward-looking endogenous interest rate and foreign exchange rate policy rules allowing for a flexible change in policy behavior. It is a gap model that allows for simultaneous identification of business cycle position and long-term equilibrium. The model was first calibrated and then its data-fit was improved using Bayesian estimation technique with relatively tight priors.